San Luis Obispo CRE Resource Center

What is CRE?
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, or CRE, is a family of germs that includes common species like E. coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Often, these germs are found in the gut. But, it can spread like an infection. To fully understand what CRE is, it’s important to understand what carbapenems are. These are antibiotics that are used to treat serious infections, usually as a last resort. As their name implies, CRE are resistant to these drugs, sometimes making treatment very difficult.
Why Is It a Problem?
As mentioned above, CRE are resistant to our most powerful antibiotics. That means if they spread from person to person, they could cause something of an epidemic. Fortunately, with enough time, doctors can find an antibiotic that is effective against the CRE, as fully resistant germs are rare. However, if waiting is not an option, there are other treatments available.
Who is Usually Affected?
In general, people who are in good health aren’t affected by CRE. It is those who have chronic health problems that are at the most risk. For one, those who are sick generally have a weaker immune system, which allows CRE to thrive. And secondly, a common way CRE are spread is through medical equipment like ventilators or catheters. If one person is affected, it can spread to people who come in contact with that person’s wounds or stool.
Noteworthy Cases
CRE infections are a somewhat new problem. This is because as we as a society sanitize everything more and more and use more antibiotics, the germs that survive become “superpowered.” They develop enzymes that prevent the antibiotics from damaging or killing the germ itself. As such, CRE are becoming a more prevalent issue.
The main epicenter for these infections is California. There has been one major outbreak at the Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles in 2015. It left two dead, five infected and at least a 200 others at risk. CRE have been cropping up in other parts of the nation as well.

How to Know If You’ve Been Infected
If you were treated at a hospital like UCLA where CRE infections have cropped, a few things will happen:
- Receive a letter in the mail from Cedar Senai, UCLA or another hospital.
- The letter states that you may have been exposed to the CRE bacteria. Generally these letters do not state how you were exposed to the CRE bacteria.
- In order to examine whether or not you have been exposed to the bacteria, you will receive a test kit in the mail.
- The test kit comes separately.
- The kit has instructions on how to take a biological sample to send it back to the hospital for testing.
- The testing confirms whether or not you have a CRE infection.
- If you test positive for CRE, you will be notified, and immediately begin treatment in the form of antibiotics.
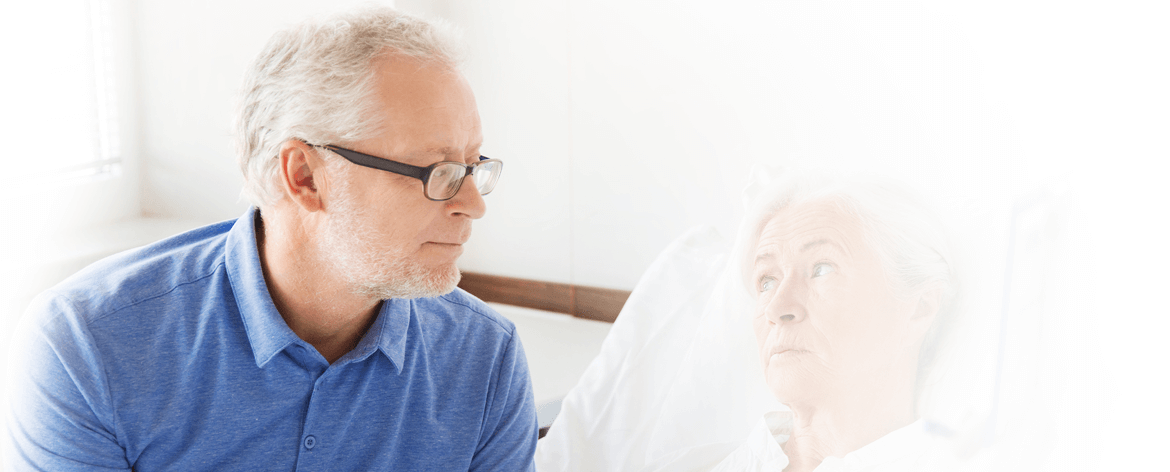
What to Do If You’ve Been Infected
Unfortunately, treating a CRE infection can be quite difficult. In fact, it has a 50 percent mortality rate. The best thing you can do is listen to every instruction your health care provider gives and follow it to the letter. There are new treatments emerging from the CDC, but they are still in the experimental stage. These, combined with traditional treatment, could be your best bet.
You should also get in contact with an experienced attorney. More often than not, CRE infections are associated with a medical procedure. That means the hospital staff may have done something wrong and caused it. An attorney can examine your case and help you figure out the next steps to take.
Our Recent Victories
Contact Us Today for a Free Consultation
How Can Ernst Law Group Help?
Schedule your free consultation by calling 805-541-0300 or contact us online to learn about the legal services we can offer you.